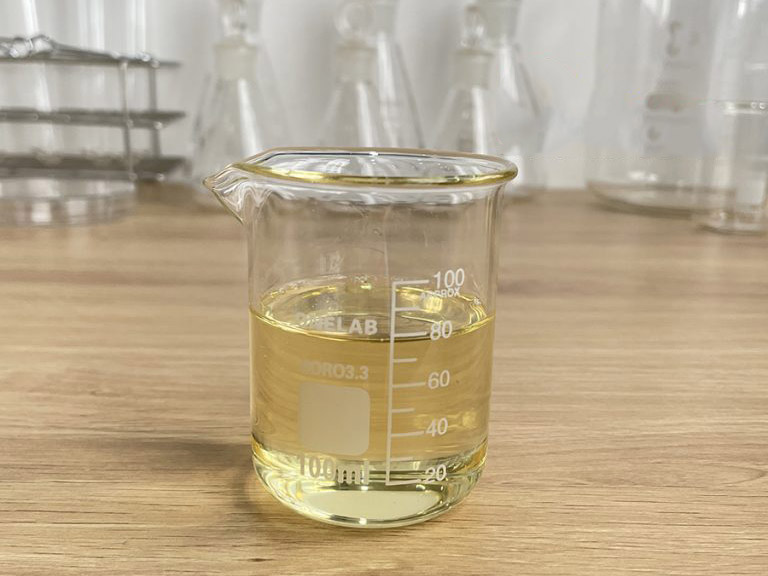
What is Cardanol?
Cardanol is an organic compound derived from cashew nut shell liquid (CNSL). It is a type of phenolic lipid, which is the main component of CNSL, and is obtained from the processing of cashew nuts. Cardanol has many applications across various industries due to its unique chemical and physical properties.
Cardanol plays a significant role in many industries due to its unique features and environmental benefits.



Characteristics and Structure
- Chemical Structure: Cardanol is a natural phenol with a long hydrocarbon chain (C15H27) attached to a phenol ring (C6H4OH).
- Source: It is extracted from anacardic acid in CNSL, a byproduct of cashew nut processing.
Applications of Cardanol
Cardanol is widely used in several industrial fields due to its superior features such as heat resistance, chemical resistance, and compatibility with various polymers:
Production of Plastics and Polymers:
- Cardanol is a key ingredient in the production of epoxy and phenolic resins, improving the mechanical and thermal properties of these products.
Lubricants and Industrial Oils:
- It is used as a component in industrial oils and lubricants due to its antioxidant and anti-wear properties.
Friction Materials:
- Cardanol is used in the manufacture of brake linings and clutch facings due to its heat resistance and wear resistance.
Paints and Coatings:
- It is utilized in paints and coatings for its ability to enhance adhesion, chemical resistance, and waterproofing.
Surfactants:
- Cardanol is used in the production of surfactants, dispersing agents for water-based inks, and cleaning agents.
Benefits and Environmental Impact
- Environmentally Friendly: Cardanol is a natural product derived from renewable resources and is less toxic compared to many industrial chemicals.
- Waste Reduction: Utilizing cardanol from cashew nut shells helps reduce waste and maximizes the use of resources from the cashew tree.






